• Overview of Large Language Models (LLMs):
• ChatGPT-4o (OpenAI, released May 2024) and Gemini Advanced (Google, evolved from Bard) are advanced LLMs with multimodal capabilities, processing text, images, and audio.
• ChatGPT-4o offers human-like reasoning with rapid response times (232-320 ms for audio inputs) and improved performance in non-English languages.
• Gemini Advanced uses the Gemini 1.5 Pro algorithm with a one-million-token context window, enabling analysis of large documents and images.
• Study Design:
• Exploratory analysis of 50 retinal pathology cases (27 surgical, 23 medical) using optical coherence tomography (OCT) and OCT angiography (OCTA) scans.
• Scans were input into ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced interfaces with the prompt: “Please describe this image”, followed by “Can you suggest a diagnosis?” if needed.
• Diagnoses classified as: Correct, Partially correct, Wrong, Unable to assess exam type, or Diagnosis not given.
• Two retina specialists independently evaluated responses.
• Key Findings:
• ChatGPT-4o outperformed Gemini Advanced in diagnostic accuracy:
• Correct/partially correct diagnoses: ChatGPT-4o: 64% (32/50) vs. Gemini Advanced: 36% (18/50) (P=0.0048).
• Surgical retina: ChatGPT-4o: 52% (14/27) vs. Gemini Advanced: 30% (8/27) (P=0.04).
• Medical retina: ChatGPT-4o: 78% (18/23) vs. Gemini Advanced: 43% (10/23) (P=0.016).
• Gemini Advanced failed to provide answers in 24% of cases (12/50), stating limitations like “That’s not something I’m able to do yet.”
• Primary misdiagnosis for both: Macular edema (ME) (ChatGPT-4o: 16%, Gemini Advanced: 14%).
• OCTA challenges: Gemini Advanced misidentified OCTA scans as non-diagnostic (e.g., “artworks,” “Lichtenberg figures”) without corresponding B-scans, while ChatGPT-4o correctly identified OCTA scans and diagnosed macular neovascularization in 4/5 cases.
• Specific Diagnostic Performance:
• Surgical Retina:
• Retinal detachment (RD): ChatGPT-4o: 60% correct; Gemini Advanced: 0% correct, with errors including ME and optic nerve head misidentification.
• Vitreomacular traction: ChatGPT-4o: 100% correct; Gemini Advanced: 33% correct.
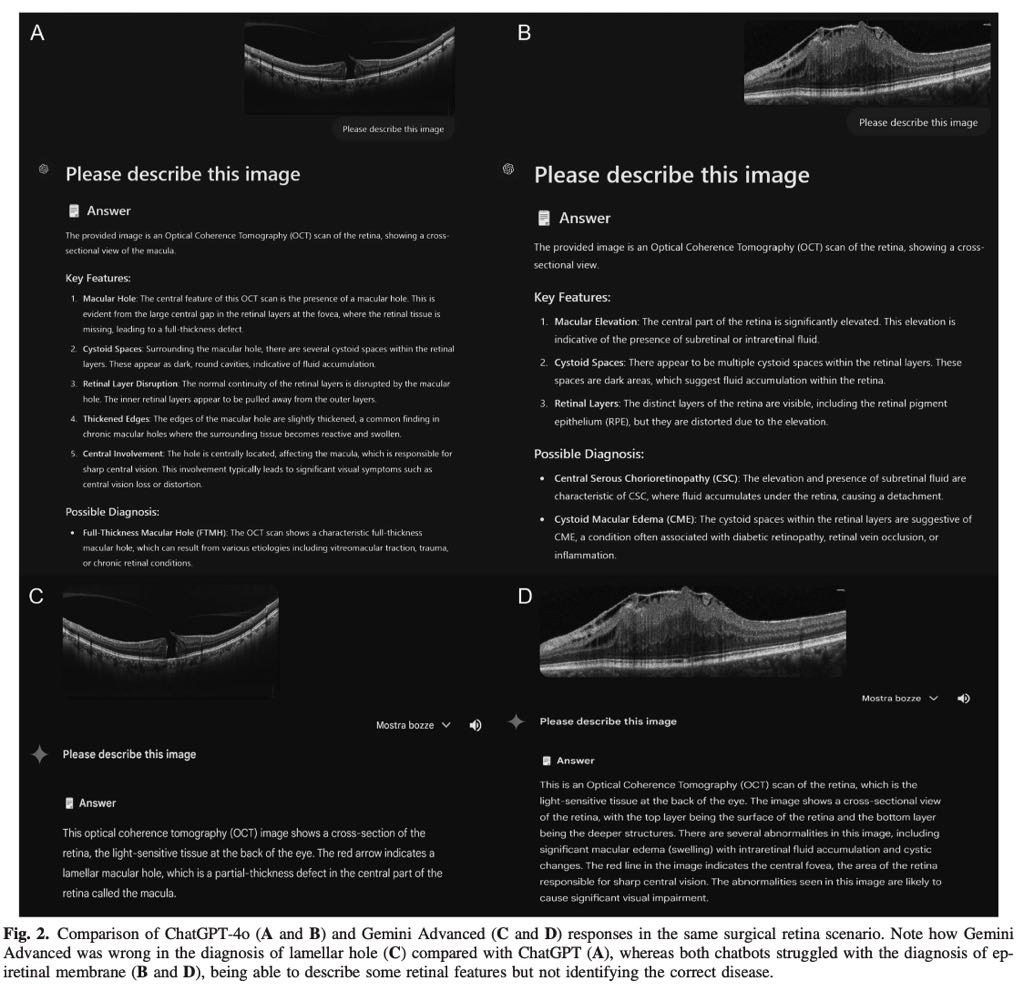
• Lamellar hole: ChatGPT-4o: 0% correct (misdiagnosed as full-thickness macular hole [FTMH] or ME); Gemini Advanced: 33% correct.
• Full-thickness macular hole: ChatGPT-4o: 80% correct; Gemini Advanced: 60% correct.
• Epiretinal membrane: ChatGPT-4o: 40% correct; Gemini Advanced: 20% correct, often confused with ME.
• Complex conditions (e.g., myopic staphyloma, retinoschisis, macular hole RD, macular fold): Both struggled, often missing key features.
• Medical Retina:
• Neovascular AMD (OCT): ChatGPT-4o: 60% correct; Gemini Advanced: 40% correct.
• Neovascular AMD (OCTA): ChatGPT-4o: 80% correct; Gemini Advanced: 0% correct without B-scans, 40% with B-scans.
• Nonexudative AMD: ChatGPT-4o: 100% correct; Gemini Advanced: 33% correct.
• Geographic atrophy: ChatGPT-4o: 50% correct; Gemini Advanced: 50% correct.
• Diabetic macular edema: ChatGPT-4o: 67% correct; Gemini Advanced: 33% correct, often missing diabetic features.
• ME (Irvine-Gass syndrome/RVO) and central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC): Both 100% correct.
• Both correctly identified healthy macula in all control cases (5/5).
• Clinical Implications:
• ChatGPT-4o shows promise for OCT/OCTA analysis but is limited to common diagnoses and less reliable for complex or rare conditions.
• Gemini Advanced requires significant updates for medical imaging, particularly OCTA, due to frequent inability to recognize diagnostic images.
• Multimodal input (text, images) is a potential turning point for AI in ophthalmology, but optimization for medical imaging is needed.
• LLMs cannot replace ophthalmologists but may assist in telemedicine or preliminary screening with further refinement.
• Limitations:
• Small sample size (50 cases) and arbitrary case selection may not represent all retinal pathologies.
• Tested initial releases of ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced, potentially underestimating future capabilities.
• Focused only on OCT/OCTA, excluding other imaging modalities (e.g., fundus photography, fluorescein angiography).
• Lack of clinical history limited diagnostic context, unlike real-world practice.
• Excluded rarer diseases due to poor performance on common pathologies.
• Future Directions:
• Further studies should test broader imaging modalities and include clinical history for context.
• Optimization of LLMs for medical imaging analysis and integration with clinical workflows is crucial.
• Potential for LLMs in telemedicine and education with improved accuracy and training.
### Citation
Carlà MM, Crincoli E, Rizzo S. Retinal imaging analysis performed by ChatGPT-4o and Gemini Advanced: The turning point of the revolution? *Retina*. 2025;45:694-702. doi:10.1097/IAE.0000000000004127