ویترکتومی در درمان اسکایزیس شبکیه در زمینه سندرم پاپیلورنال
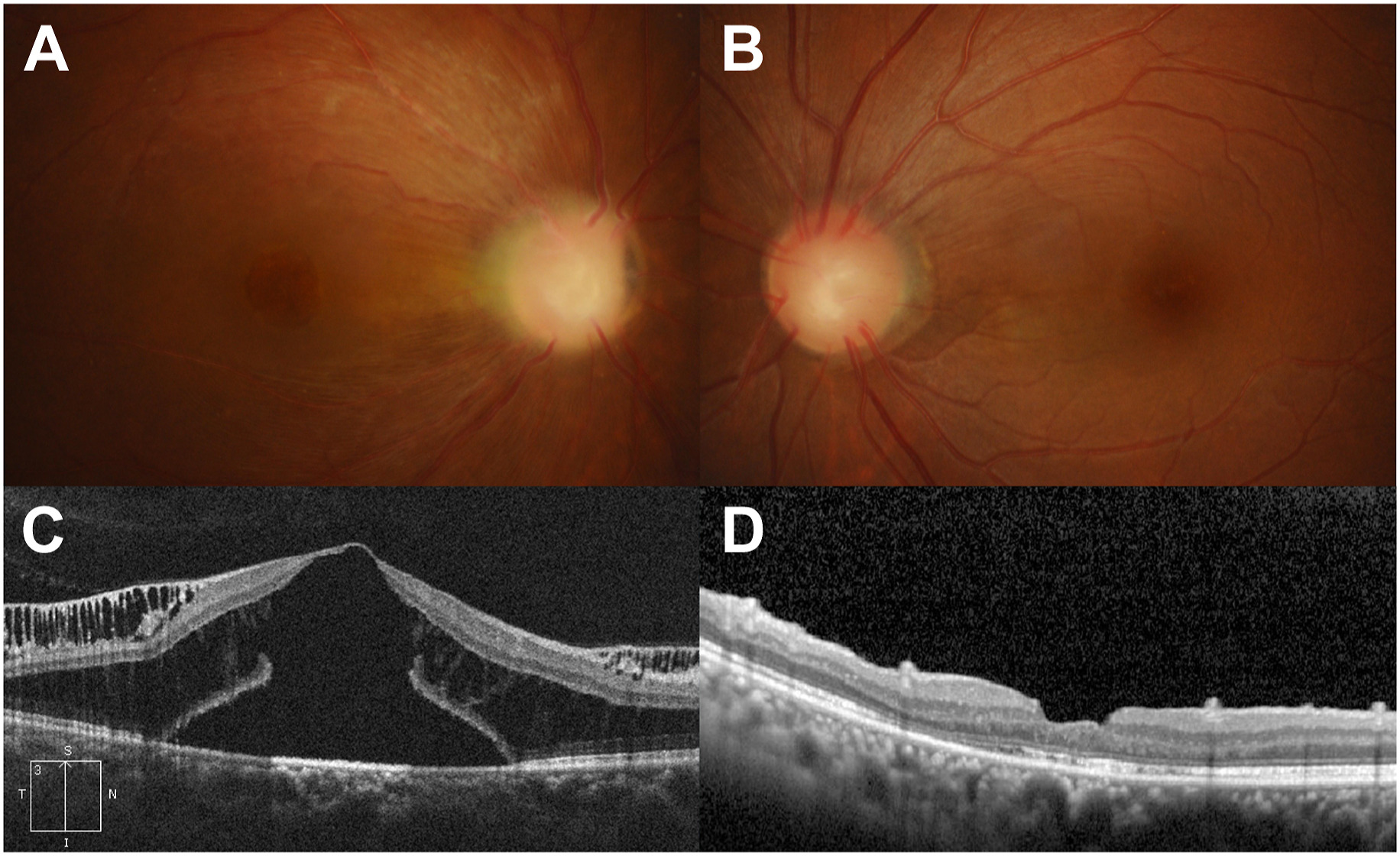
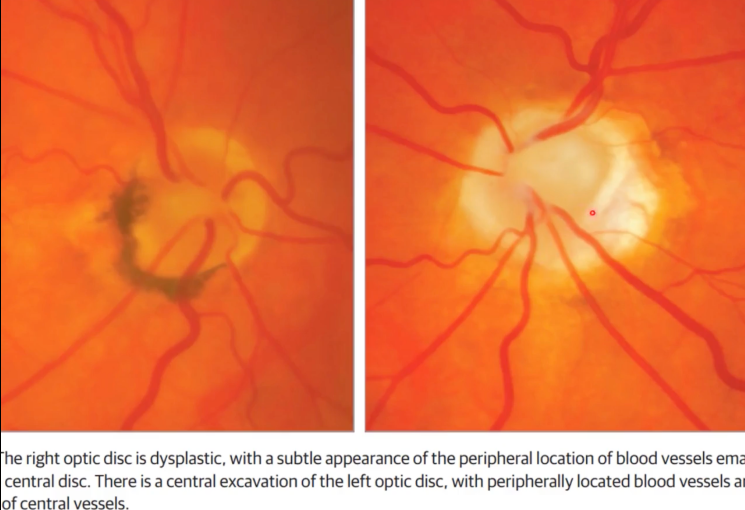
A female patient, aged 36, who has previously undergone a kidney transplantation, presented with visual impairment specifically affecting the right eye. The right eye exhibited optic disc excavation, the absence of central retinal vessels, a multitude of cilioretinal vessels, and macular thickening (A and B).
The presence of a PAX2 mutation was verified through genetic testing.
The optical coherence tomography (OCT) examination revealed the presence of schisis in the outer plexiform and nerve fiber layers, as well as foveal detachment accompanied by an outer macular hole (C).
The individual underwent vitrectomy and the subsequent insertion of a gas tamponade. The reattachment of the retina occurred one year following the surgical procedure (D), resulting in an enhancement of the final visual acuity in the right eye from 20/200 to 20/63.